 There have been separate cases of Equine Influenza confirmed in the UK. Horses in Essex, Cheshire and Derbyshire have been affected this month with further reports of outbreaks in Belgium, France and Germany. With all three outbreaks it has been unvaccinated horses that have tested positive.
There have been separate cases of Equine Influenza confirmed in the UK. Horses in Essex, Cheshire and Derbyshire have been affected this month with further reports of outbreaks in Belgium, France and Germany. With all three outbreaks it has been unvaccinated horses that have tested positive.
Currently the number of outbreaks is small but they have occurred within a short duration; to put things into perspective a similar number of cases were reported during the whole of 2018.
It is currently unknown which strain of the virus has caused these outbreaks, but research is being conducted to find out. While there are several signs of flu in horses, those affected may only show one or two of them.
What are the signs of infection?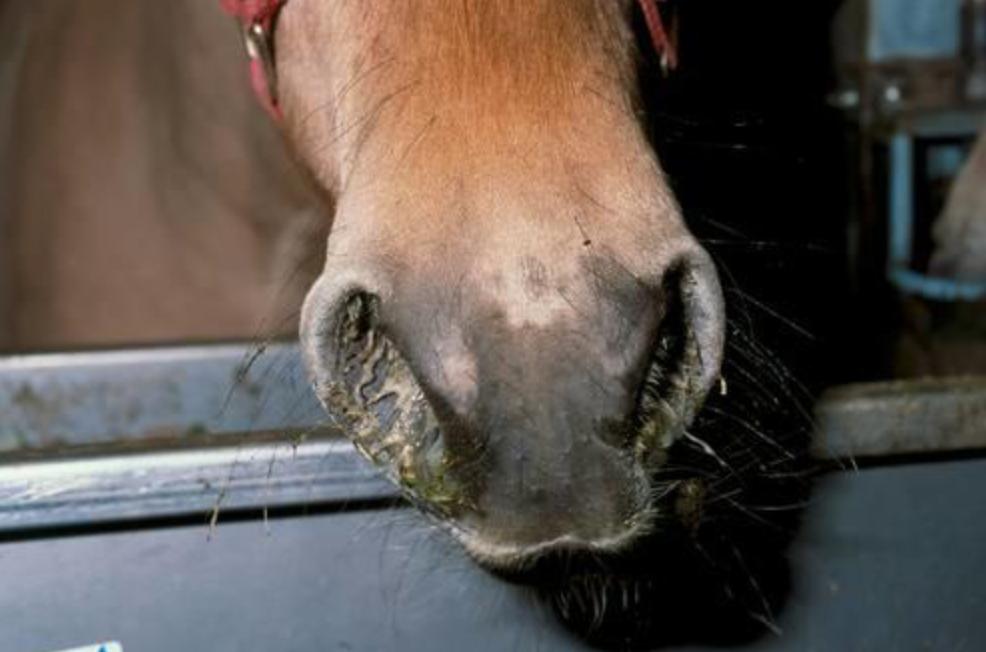
Unvaccinated horses
- In unvaccinated horses the virus targets the upper respiratory tract, this leads to a very dry, harsh or hacking cough.
- They usually have a raised temperature which can last around 7-10 days. The fever often makes them dull, off their food and lethargic
- A clear or white nasal discharge is often seen with enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes (under their chin/throat area).
Vaccinated horses
- Horses that have been regularly vaccinated often show no clinical signs, but they may still shed enough virus to infect other horses. This is how the outbreak in Australia in 2007 started.
- Horses that have been vaccinated but only have partial protection, e.g. because they haven’t been vaccinated frequently enough or because the vaccine type used was not updated, may show varied signs of mild non specific respiratory disease. This can include mild lethargy, nasal discharge and possibly a cough.
What to do if you think there is a possible infected horse?
Owners should seek veterinary advice if they suspect there is flu on the yard and carry out the following precautions:
- Isolate the possibly infected horses. Infected horses will spread the virus in respiratory droplets, through coughing, and can spread the virus for up to 10 days. They must be isolated until the vet advises they are no longer infected.
- All horse movements on and off the yard should be stopped.
- Monitor all horses on the yard for clinical signs and record their rectal temperature daily, it should be less than 38.0˚C. A rise in temperature can be an early sign of an infection.
- Booster vaccinating all in-contact horses, even if they are not yet due their annual booster, has been shown to provide horses with even more protection against flu.
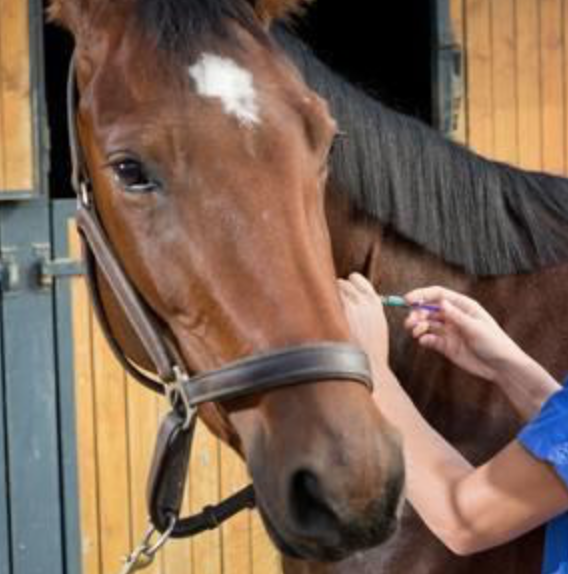
 Horse Flu is endemic in the UK, which means that most horses will come into regular contact with the virus during their lifetime. The control of horse flu in the UK is based on limiting the signs of infection in horses that have been exposed to the virus, rather than trying to prevent exposure itself. This is primarily achieved through regular vaccination which is given either once or twice a year.
Horse Flu is endemic in the UK, which means that most horses will come into regular contact with the virus during their lifetime. The control of horse flu in the UK is based on limiting the signs of infection in horses that have been exposed to the virus, rather than trying to prevent exposure itself. This is primarily achieved through regular vaccination which is given either once or twice a year.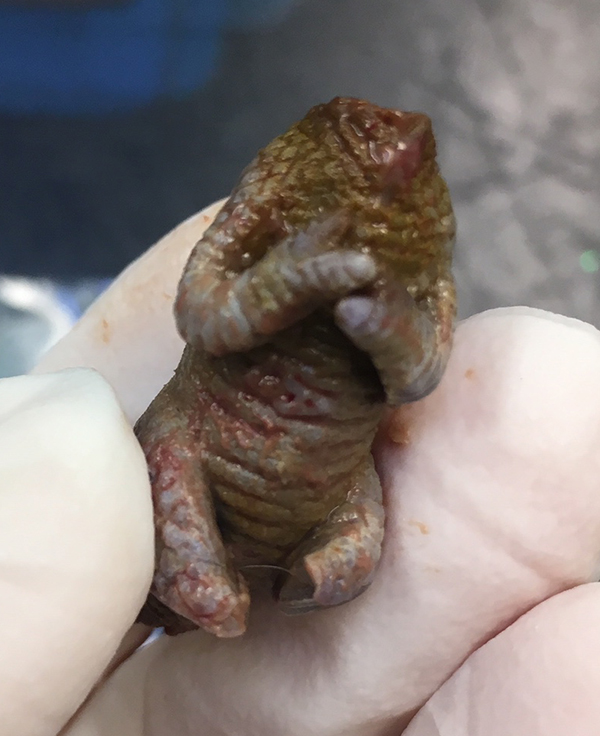

 We currently have a horse crisis, whereby the number of horses far outweighs the number of good homes available.
We currently have a horse crisis, whereby the number of horses far outweighs the number of good homes available.
 Border disease or hairy shaker disease is a virus which causes birth defects, barren ewes and abortion. It is from the same family of viruses as BVD in cattle.
Border disease or hairy shaker disease is a virus which causes birth defects, barren ewes and abortion. It is from the same family of viruses as BVD in cattle. The signs are very similar to chronic pneumonia:
The signs are very similar to chronic pneumonia: