The Big Five Diseases in Sheep
Maedi Visna
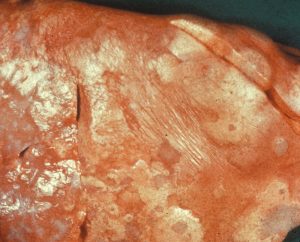 Maedi Visna is a wasting disease causing chronic pneumonia. It is caused by a highly contagious virus. Most sheep are infected as lambs via colostrum or aerosol, however generally do not show signs until they are 4 years old.
Maedi Visna is a wasting disease causing chronic pneumonia. It is caused by a highly contagious virus. Most sheep are infected as lambs via colostrum or aerosol, however generally do not show signs until they are 4 years old.
The main signs are:
[checklist icon=”fa-arrow-circle-right” iconcolor=”#39aa87″ circle=”yes”]
- Thin ewes/wasting away
- Pneumonia
- Mastitis
- Arthritis
- Reduced fertility
- Smaller weaker lambs which grow poorly due to a lack of milk
[/checklist]
Blood tests are commonly used to diagnose MV. Selecting thin cull ewes to test will help identify the disease if present within the flock.
If you suspect MV in your flock or wish to know your MV status we can do a 12 cull ewe screen.
Please call 01772 861300 to discuss.
Ovine Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma – OPA
 Ovine Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma is caused by a virus leading to a progressive and fatal infectious lung cancer of sheep. The virus is spread from infected sheep by aerosol and nasal discharge. It is often seen in older thin sheep. There is no treatment.
Ovine Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma is caused by a virus leading to a progressive and fatal infectious lung cancer of sheep. The virus is spread from infected sheep by aerosol and nasal discharge. It is often seen in older thin sheep. There is no treatment.
The signs are very similar to chronic pneumonia:
[checklist icon=”fa-chevron-circle-right” iconcolor=”#39aa87″ circle=”yes”]
- Difficulty breathing
- Weight loss
- Excessive watery fluid from the nose
- Sudden death
- Secondary infections such as Pasteurella are common.
[/checklist]
Once signs are evident the disease is fatal.
The definitive diagnosis is made by post mortem examination of the lungs.
If there is suspected OPA ultrasound examination of the lungs can be considered.
Johne’s Disease
 Johne’s disease is caused by a bacterium which grows very slowly and lives for a long time in the environment. It is mainly spread through faecal contamination of feed and the environment, ewes also pass it to their lambs across the placenta and in colostrum. It is the same agent that causes Johne’s disease in cattle.
Johne’s disease is caused by a bacterium which grows very slowly and lives for a long time in the environment. It is mainly spread through faecal contamination of feed and the environment, ewes also pass it to their lambs across the placenta and in colostrum. It is the same agent that causes Johne’s disease in cattle.
Infection generally occurs early in life, sheep often do not show signs for years and act as carriers, these are referred to as ‘sub-clinically infected’.
Affected sheep suffer from:
[checklist icon=”fa-chevron-circle-right” iconcolor=”#39aa87″ circle=”yes”]
- Severe weight loss
- Sudden death
- Anaemia
- High parasite burdens
- Affected flocks suffer from poorer production, more thin ewes and increased culling.
[/checklist]
Testing for Johne’s can be tricky at an individual level. There is no single diagnostic test that can detect the disease at all the stages and sub-clinically infected animals may test negative.
Blood screening groups of cull/thin ewes can be effective at identifying Johne’s disease in your flock.
Border Disease
 Border disease or hairy shaker disease is a virus which causes birth defects, barren ewes and abortion. It is from the same family of viruses as BVD in cattle.
Border disease or hairy shaker disease is a virus which causes birth defects, barren ewes and abortion. It is from the same family of viruses as BVD in cattle.
If a ewe is infected during pregnancy the virus passes through the placenta to the lamb, in some cases this causes embryonic loss or abortion. Some lambs survive and are born Persistently infected (PI). PIs shed the virus continuously and can infect other sheep and lambs. This can be a major problem in naïve flocks unknowingly buying in PIs which can then cause around half of lambs born to be affected by the disease.
[checklist icon=”fa-chevron-circle-right” iconcolor=”#39aa87″ circle=”yes”]
- Infection in non-pregnant adult sheep is generally short lived and mild, often no clinical signs are seen.
- Hairy shakers are lambs infected with the virus whilst developing in-utero effecting their nervous system which leads to trembling and incoordination. They also have long curly wool.
- Some lambs are born completely normal but maintain the infection, these are called Persistently Infected animals (PI).
[/checklist]
Hairy shakers are usually a good way to diagnose the presence of the disease. These lambs can also be blood tested to confirm presence of the virus.
Blood testing a group of ewes can identify if the flock has been exposed to the disease and is likely to be present.
Caseous Lymphadenitis – CLA
 CLA is a chronic bacterial infection of the lymph nodes resulting in abscesses. The bacteria often enters via cuts and is commonly spread through close contact when animals are housed or are trough fed. The disease can also be transmitted indirectly such as on shearing equipment.
CLA is a chronic bacterial infection of the lymph nodes resulting in abscesses. The bacteria often enters via cuts and is commonly spread through close contact when animals are housed or are trough fed. The disease can also be transmitted indirectly such as on shearing equipment.
[checklist icon=”fa-chevron-circle-right” iconcolor=”#39aa87″ circle=”yes”]
- Infected animals have lumps often behind the jaw, in the arm pit and in the groin. These lumps are often cold and painless but can burst open and drain pus. Once they have healed and scarred over the abscess can re-occur.
- Abscesses also form inside the sheep causing ill-thrift and weight loss.
[/checklist]
Lumps and abscesses are a classic sign of the disease and should not be ignored.
Diagnosis is either by sampling the intact abscesses and culturing the pus or by blood test.
